Data Binding in Android
What and why?
One way to manipulate things in a layout is to use fineViewById(R.id.xxx) to find elements at runtime and do stuff, which can be slow for complex layouts.
Another option is to connect layout to Activity or Fragment using Data Binding. (This gives performance enhancements)
Data binding is a pattern to solve the above-discussed problem by, connecting layout to activity/fragment at compile time.
The compiler creates a helper class when the activity/fragment is created called the binding Class.
How?
- Enable data binding in build.gradle.
android {
...
buildFeatures {
dataBinding true
}
}2. wrap layout xml in a <layout> xml tag, that will contain the view groups & views.

3. Import the Binding class created by the compiler. The binding class’s name is derived from the name of the layout file.
activity_main.xml → ActivityMainBinding4. Create a late init var binding in the Activity/fragment and initialize it using the binding class generated by the compiler. → This happens in onCreate() for activity
binding = DataBindingUtils.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main)
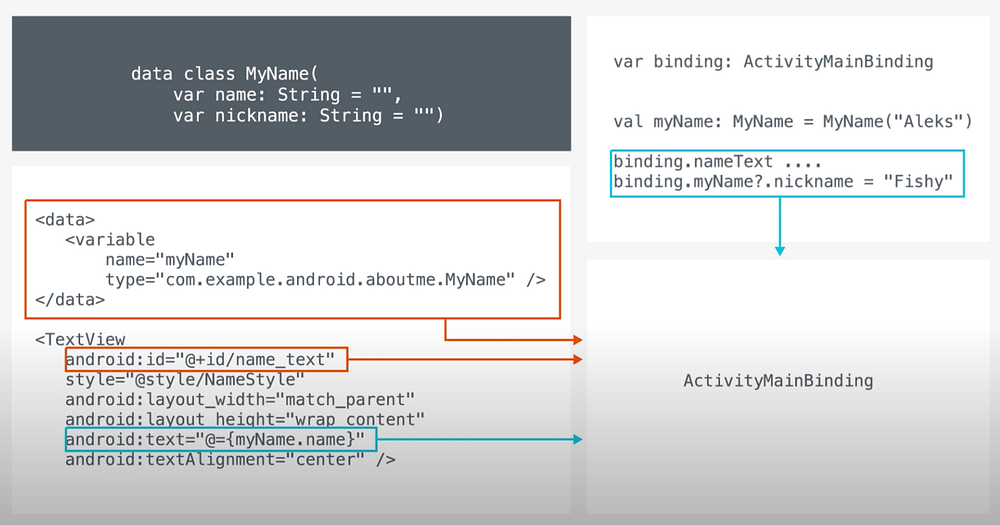
Data binding can not only be used to access view elements on activity/fragment but can also provide a data object to views (to be used directly in XML layout)
Create a data class, let layout know about the data class using <variable> then instantiate the object in the Activity/Fragment. (Again in onCreate() for activity)